Omega-3 deficiency during pregnancy: a dangerous and common condition especially among the weaker sections of the population

Omega-3 deficiency in pregnancy: dangerous and common!
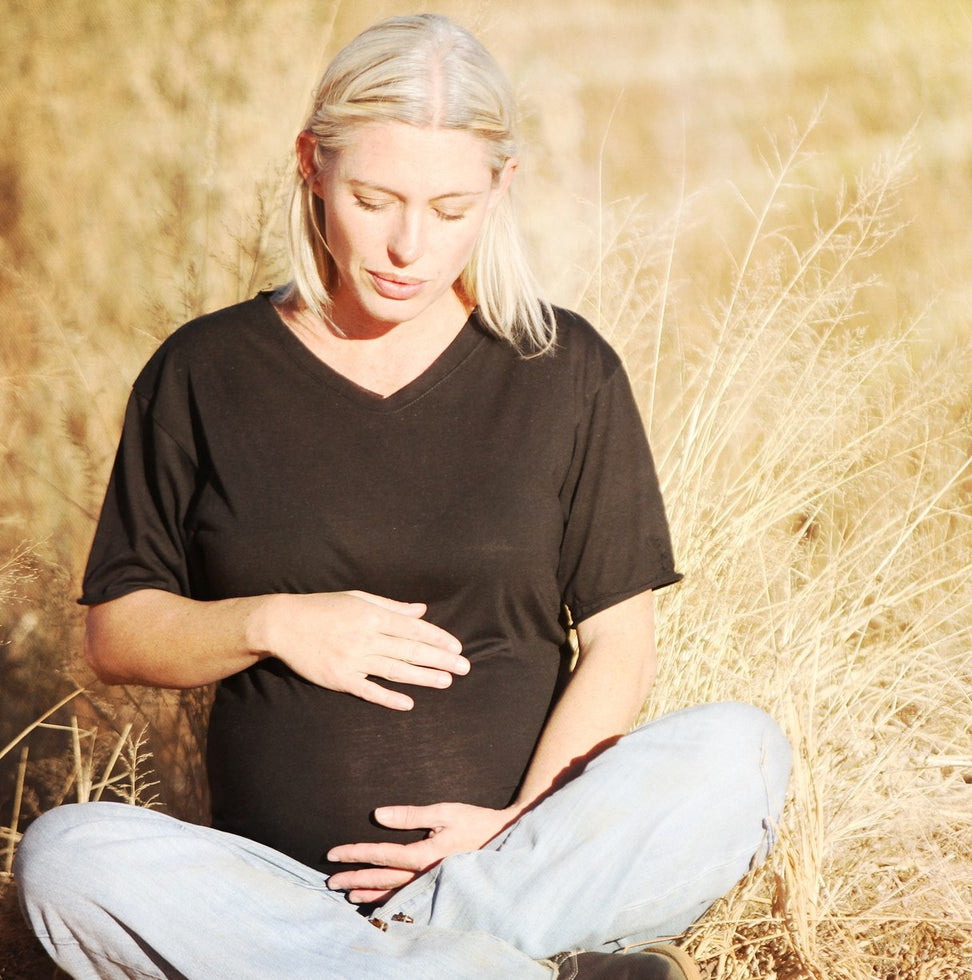
Despite the well-known benefits of omega-3 during pregnancy, many women do not consume enough EPA and DHA during gestation, putting their health and that of their babies at risk. Omega-3s are essential for the proper course of pregnancy and to ensure fetal development. According to a recent American study, pregnant and childbearing-age women consume an average of only 89 milligrams of EPA and DHA per day, a quantity far too low compared to the daily requirement. The most concerning data especially regards women from weaker socio-economic backgrounds. The entire research, conducted by scientists from the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha (USA), was recently published in the journal Nutrients.
Omega-3 in pregnancy: essential for fetal and maternal health
Maternal nutrition is crucial during gestation to ensure healthy fetal development, maternal health, and the proper course of pregnancy.
Several studies have shown that the quantity and quality of fatty acids consumed during pregnancy deeply influence the growth and development of the baby.
In particular, omega-3s consumed by pregnant women through proper nutrition have been associated with a lower risk of maternal depression, reduced rates of intrauterine growth restriction and preterm birth, as well as a lower risk of allergies and asthma in children, and better neurocognitive outcomes in offspring.
DHA is the main polyunsaturated fatty acid found in the human brain and retina rods, and is essential for fetal brain and retinal development during pregnancy, and for psychomotor and visual development of the child in the first months of life. Many studies conducted in recent years have shown the health benefits of these fatty acids, and numerous research groups have proposed recommendations on omega-3 intake based on age, health, and other factors.
Daily recommendations for omega-3 intake vary widely, probably due to the broad range of dosages used in clinical studies investigating the positive actions of these fatty acids. In any case, the general consensus suggests a minimum dose of 200 milligrams per day of EPA and DHA. For example, during pregnancy and breastfeeding, the World Health Organization recommends consuming 200-500 mg per day of EPA and DHA.
According to EFSA (European Food Safety Authority) and LARN 2014 (Reference Intake Levels of Nutrients and energy for the Italian population), the DHA requirement increases by 100-200 mg per day during pregnancy and breastfeeding, in addition to the 200 mg daily omega-3 (EPA and DHA) requirement; this is based on studies showing that increased DHA in breast milk coincides with better overall infant health, especially in cognitive development and visual acuity. Also, fish plays an important role in the diet of breastfeeding women. To provide an adequate amount of DHA, at least 2 portions of fatty or semi-fatty fish per week are needed, up to a maximum of 3-4 portions.
The choice of fish for nursing mothers should focus on those rich in EPA and DHA and low in environmental contaminants such as mercury. Small fish such as sardines, anchovies, and mackerel are preferred over large fish, which tend to accumulate more contaminants. Despite the importance of these fatty acids in maternal-fetal health, omega-3 intake during pregnancy is typically very low in the Western diet and is influenced by socioeconomic factors shown to impact overall diet quality, particularly fruit and vegetable consumption.
Low omega-3 intake during pregnancy for most American women
The aim of this study was to use data collected from a national survey (NHANES) to investigate omega-3 intake in women of childbearing age in the United States, and to assess the impact of poverty, race, food security, and other socioeconomic factors on these nutrients. According to the survey results, the amount of DHA consumed by pregnant and non-pregnant women was 66 mg and 58 milligrams per day, respectively. These doses do not include omega-3 from dietary supplements; other data indicate that only 9% of pregnant women had taken EPA and/or DHA supplements and only 1.8% of non-pregnant women.
Among the women examined, researchers found that omega-3 intake decreased as poverty increased, and women with university education had higher omega-3 levels compared to those with lower education. "Our results show that low omega-3 intake should be a concern for pregnant and childbearing-age women in the United States and that the most vulnerable groups are more susceptible to deficiencies," researchers stated in Nutrients, emphasizing the need for targeted strategies to increase omega-3 intake to improve maternal and infant health. Independently commenting on the study’s conclusions, Harry Rice, Vice President of the EPA and DHA organization (Goed), stated that these results come from well-designed research and suggest the benefits of EPA and DHA supplementation for pregnant women, particularly in reducing the risk of preterm birth. As experts know, carrying pregnancy to full term strongly increases the chance of good health after birth, highlighting how omega-3 intake is crucial for pregnant women. Current research underscores the need to encourage EPA and DHA intake through fish consumption and/or supplementation with quality supplements.
Key study details
Scientists used data from 7,266 women who participated in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) collected between 2003 and 2012. Of these, 6,478 were women of childbearing age, and 788 were pregnant at the time of the survey. Nutritional status data indicated an average EPA and DHA intake of 89 mg, with no significant differences between pregnant and non-pregnant women.
Analyzing the numbers by subgroups, researchers found omega-3 intake was associated with women's socio-cultural level and ethnicity. Non-Hispanic white women of childbearing age had the lowest EPA and DHA levels, with an average value of 78 mg per day, compared to Hispanic women (94 mg), non-Hispanic black women (112 mg), and women of other or multiracial ethnicities (142 mg).
Many factors appear to contribute to these dietary disparities, including the high cost of healthier foods in the United States. Individuals from poorer families are less likely to consume fruits and vegetables and are more prone to buy foods high in fats and sugars, increasing the likelihood of nutritional deficiencies. Use of vitamin and omega-3 supplements is also very rare in these populations.
Intervention programs for vulnerable populations
In conclusion, the data highlight the need to encourage American women to consume more EPA and especially DHA. Further study is needed to determine which interventions are best suited for specific populations, particularly low-income groups who tend to have higher body weight and follow poor-quality diets, with negative outcomes for infant and maternal health. As the researchers emphasized, "As the U.S. population becomes increasingly diverse, health and dietary disparity issues become even more relevant."
Vita DHA materna: the specific supplement for pregnancy
VitaDHA materna is the supplement offered by U.G.A. Nutraceuticals dedicated to the health of mother and child. One softgel contains 350 milligrams of omega-3 and 400 micrograms of highly bioavailable folic acid.
Source:
T.M. Nordgren et al. “Omega-3 Fatty Acid Intake of Pregnant Women and Women of Childbearing Age in the United States: Potential for Deficiency?” Nutrients ; 2017, 9(3).
Recommended products
VitaDHA Maternal
The most beautiful journey deserves the best possible ally. VitaDHA® Materna is the supplement specifically designed for the most important experience of your life: each pearl contains 450 mg of DHA Plus® for the development of your baby's brain and vision, combined with Quatrefolic®, a new generation folate three times more absorbable than traditional folic acid. From pre -conception to breastfeeding, a superior formula that combines maximum bioavailability with ease of intake.
Serving size : 1
Number of servings : 30
Lot and expiry : 5983255 - September 2027
Ferrolip Forte
Maximum absorption, no gastric discomfort. Ferrolip® Forte uses microencapsulation technology to “escort” iron directly where it is needed, avoiding discomfort. And there’s more: we have enriched it with vitamin C to enhance its effectiveness, methylfolate (the most easily assimilated form of folic acid) and vitamin B12 for a complete energy boost . An advanced formula, particularly valuable for future and new mothers, in a practical orosoluble powder with a pleasant lemon flavor. Because when it comes to energy and well-being, even a single detail makes the difference.
Serving Size: 1
Number of servings: 30
Lot and expiry: J02034 - March 2028
VitaDHA liquid in vials
Having trouble with capsules? Children reluctant to take them? VitaDHA® is the answer you were waiting for. A DHA Plus® supplement in liquid form, with a delicious lemon flavor. Convenient to dose, easy to take and highly absorbable thanks to its triglyceride form: it is the perfect solution for the whole family.
Serving size: 1
Number of servings: 30
Lot and expiry: 25000070 - January 2028
OMEGOR Vitality 1000 - 90 capsules
Just 3 words: power, freshness, purity . And always 5 stars. OMEGOR® Vitality is a concentrate of Omega-3 evaluated by IFOS (International Fish Oil Standards), the most famous quality certification in the field of Omega-3 supplements, always with the maximum score since 2005, the year of its commercialization. It is the top of the range.
Serving Size: 1-4 capsules
Number of servings: 22-90
Lot and expiry: 243406 - October 2027
VitaDHA 1000 - 60 capsules
Innovation has a new flavor: it smells of lemon. VitaDHA® 1000 combines the power of DHA Plus® with the pleasure of a lemon capsule. IFOS 5-star certified, our purified, deodorized and flavored fish oil supplement is perfect for the well-being of adults and children.
Serving Size : 1-6
Number of servings : 10-60
Lot and expiry : 500530100 - July 2026
OMEGOR Veg
Omega-3 is not only found in fish, did you know? Nature offers us a precious alternative: the microalgae Schizochytrium sp, a natural source of DHA (docosahexaenoic acid) and EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid). Omegor® Veg contains and concentrates these Omega-3 in capsules certified by the Vegan Society and with IFOS 5 stars certification (the maximum), very rare in products of algal origin.
Serving Size: 1
Number of servings: 60
Lot and expiry: 246810/A - January 2027